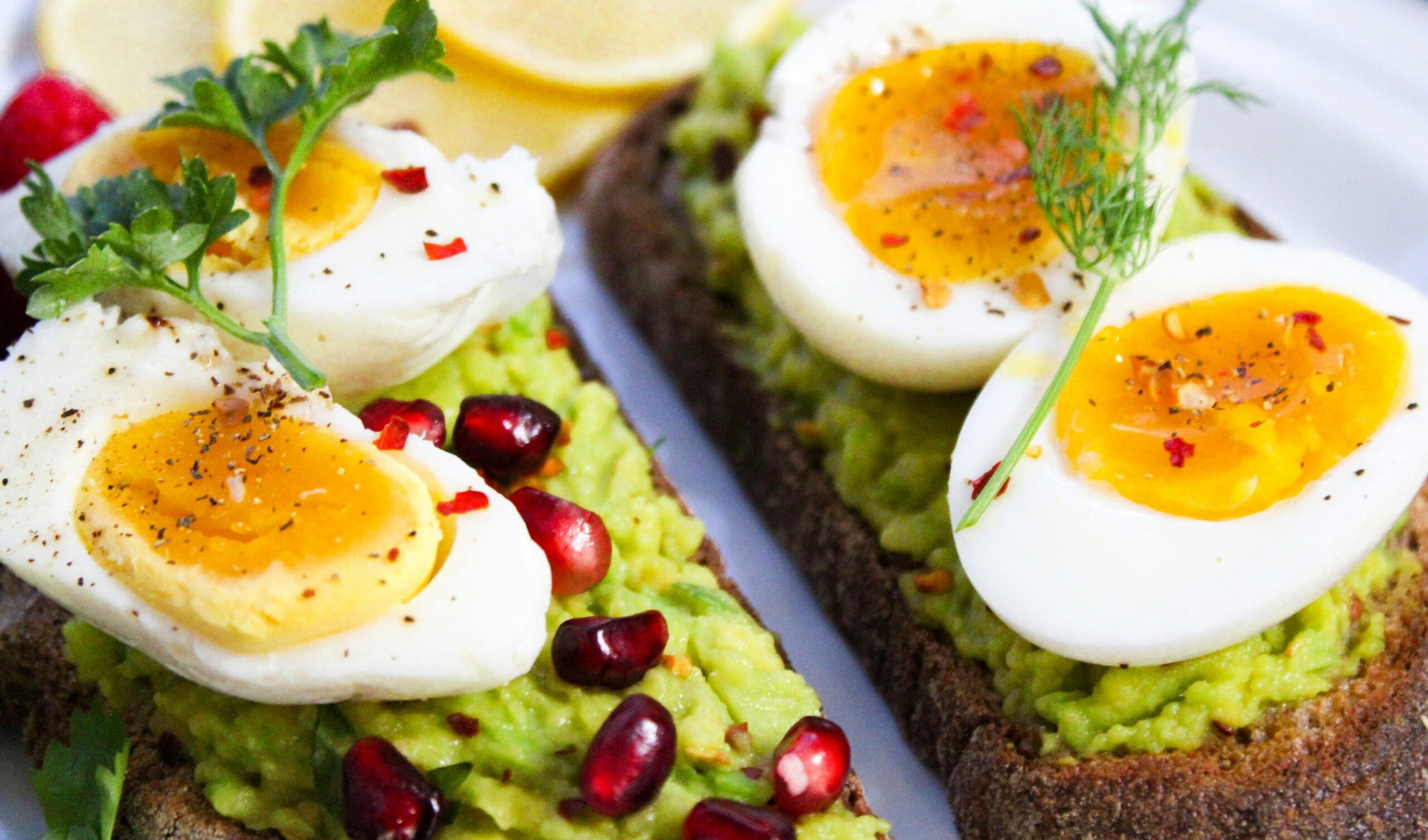
Following some specific sports nutrition guidelines is very important as it helps the body avoid injuries, replaces muscle glycogen and builds muscular mass and strength (1). It’s essential to have a meal 1 to 3 hours before training or competition as the athlete will start training or competing full of energy. Having meals during training or competition – especially during a prolonged training / competition – it’s similarly very important as the body needs to refuel as soon as possible during / after exercise to function effectively. Young athletes like swimmers or artistic swimmers need to know when, how and what to eat before during and after training – competition. They also need to know the macro nutrients and the fluids which are necessary for their body’s development, function, health and performance. Below you will find some healthy snack ideas that a swimmer or artistic swimmer can have before, during and after training or competition.
Eating Before training or competition (1 – 3 hours before) (2).
Focus on high carb, and low fibre and fat options. Consume foods you are familiar with and you have a good digestion when consuming.

- Whole grain bagel with 1 slice of chicken + 1 slice of low-fat cheese + green salad + 1 apple.
- 1 bowl of porridge with semi-skimmed milk + strawberries – blueberries on the top + 1 teaspoon honey.
- 1 bowl of pasta with chicken or tuna + fresh tomato sauce, baby tomatoes and mixed peppers.
- 1 bowl of rice with turkey mince and a small portion of peas or beans.
- 1 baguette with 1 slice smoked salmon and 1 slice of low-fat cheese + green salad.
- Fruit smoothie with 1 apple – 300 ml of semi-skimmed milk + 2-3 tablespoons of low-fat yogurt.
- 2 – 3 pancakes (preferably with whole-wheat flour or oat flour), flaxseds ground + 1 – 2 teaspoons honey + 2 – 3 raspberries on the top.
- 2 bananas and a few mixed nuts.
- Fruit salad (1 apple, 1 pear and 1 mango) + 1 pot low-fat yogurt.
- 1 big baked sweet potato or potato with cottage cheese and green salad on the side.
Eating During Training – Competition (if needed, this depends on the duration or the training-competition) (2).

- 1 – 1.5 sports energy bar.
- 2 slices of whole-wheat bread with honey and half a banana on each of them.
- 80 g (= 2 – 3 small square pieces) of dark chocolate bar.
- 2 slices of home – made cake (with whole-wheat flour and fruit e.g. blackberries, blueberries).
- 1 – 1.5 handful of dried apricots with 10 almonds and 10 walnuts.
- 2 pears.
- Low-fat yogurt with porridge and a few berries.
- 1- 1.5 handful of raisins with 10 – 20 cashews.
- 1 – 2 granola bars.
- 1 isotonic sports drink.
This snack is optional and depends on the training’s duration and each athlete’s needs. It is best to contact a registered sports nutritionist to find out how much and when you need to eat. Aim to have a good digestion with everything you eat.
Eating After Training – Competition (meals high in protein) (2).
Aim for at least 20 g of protein post-exercise (2).
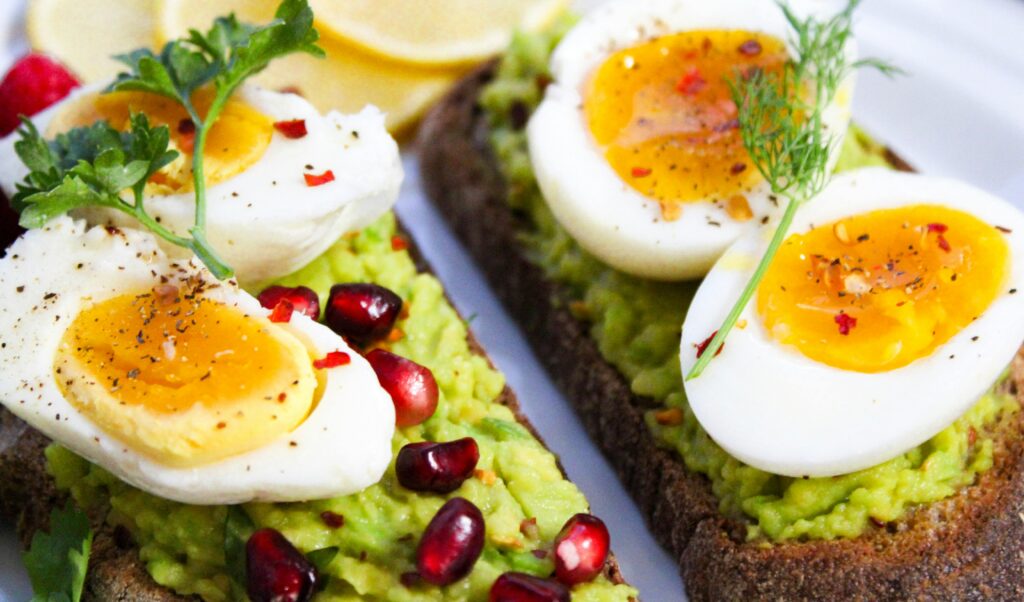


- 500 ml milk semi-skimmed or chocolate milk.
- 2 slices of whole meal bread with cottage cheese spread and sunflowers sprinkle on the top.
- 2 slices of whole meal bread with peanut butter, honey + 1 tablespoon flaxseeds on the top.
- 1 tuna sandwich with whole meal bread, cucumber and green salad.
- 1 omelet with 3 eggs, avocado, peas, asparagus, spinach and carrots.
- 1 protein yogurt (20 g protein), if plain you can add a teaspoon of honey or nuts and peanut butter.
- 1 protein bar (better homemade with seeds, nuts, any type of nut butter and dark chocolate).
- 1 smoothie (400 ml) (1/2 banana, ½ apple, 1 table spoon peanut butter, 1 table spoon flaxseeds + 250 ml of coconut milk).
- 1 jacket potato with turkey mince and grated low-fat cheese on the top. You can add a salad on the side.
- Green salad with tomato, cucumber, whole meal dried bread, halloumi cheese and 2-3 eggs.
Of course, as mentioned above it is best to contact a registered sports nutritionist, in order to find out what exactly you need to consume before, during and after training. The nutritionist will prepare a personalized nutrition plan based on your needs and he/she will educate you on how to eat healthily, change your daily habits and maintain the good habits for the long term.
This article was written by the founder of amvnutrition.com, Anna-Maria, who is a registered sports nutritionist (practitioner registrant, SENr, BDA, INDI) and a sports scientist (EIMGreece). Anna-Maria has worked with a variety of different athletes and active individuals, she is an excellent communicator and she always finds appropriate and comforting ways to helps each individual she works with. You can see more of Anna-Maria’s background here.
References
- Hark, L. and Deen, D. (2005). Nutrition for life. The definitive guide to eating well for good health. United Kingdom: Dorling Kindersley.
- Burke, L. (2007). Practical Sports Nutrition. United States of America, USA: Human Kinetics.
Anna-Maria Volanaki